The Indian rupee is the currency of India. It is the official currency of the Republic of India. The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India. The Reserve Bank manages currency in India and derives its role in currency management on the basis of the Reserve Bank of India Act, of 1934. In July 2018, the Indian rupee was ranked as the world’s sixth most traded currency.
India is a land of 1.3 billion people and counting. With the population ever-growing, the need for a more inclusive currency has become apparent. The current paper currency, the Indian rupee, is not only outdated but also unfair to those without easy access to banking institutions.
In comes the e-rupee, a new digital currency that seeks to solve these issues. The e-rupee is a more inclusive form of currency that can be accessed by anyone with a mobile phone. It’s safe, convenient, and most importantly, it’s fair. Read on to learn more about the e-rupee and how it’s poised to change the way we transact in India.
What is Central Bank Digital Currency
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) is a type of digital currency that is issued by a central bank. CBDCs are created using blockchain technology and can be used to make online payments.
CBDCs have the potential to revolutionize the way we make payments and could provide a more efficient and convenient alternative to traditional methods such as cash and checks. They could also help to reduce fraudulent activities, as each transaction would be recorded on the blockchain.
In order to use CBDCs, users would need to have a digital wallet that could be accessed via their mobile phone or computer. Once they have been verified by the central bank, they would be able to make instant payments using digital currency.
At present, there is no country that has officially launched a CBDC but several are exploring the possibility, including China, Sweden, and the Bahamas. It is expected that more countries will follow suit in the coming years as CBDCs become more popular.
But India has launched it CBDC pilot project – eRupee on 1st December
What is the e-Rupee?
In a rapidly globalizing world, the Indian rupee has been lagging behind other major currencies. However, this may soon change with the introduction of the e-rupee. The e-rupee is a new, digital version of the currency that aims to make transactions more efficient and secure issued by Reserve Bank India and backed by the Government of India.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) started a pilot project for the retail digital rupee on December 1st. Participants of the pilot would be merchants and customers in a closed user group. The e₹-R would be in the form of a digital token that represents legal tender and would be distributed through intermediaries, such as banks, just like paper currency.
e₹-R is designed as a single currency for all types of digital transactions. Users will be able to use this form of currency through a transaction network owned by banks and stored on mobile devices such as phones and tablets.
For convenience, the e₹-R could be used by scanning QR codes that are displayed by merchants. As with physical cash, these units of e₹-R won’t earn any interest and can be converted into other forms of money, like deposits at banks.
Eight banks will be joining the pilot in various phases, starting with four more at a later date. These include the Union Bank of India, HDFC Bank, Kotak Mahindra, and Bank of Baroda. Those participating in phase one are the State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Yes Bank, IDFC First Bank, and four other banks that join at a later date.
The first phase will cover four cities including Mumbai, New Delhi, Bengaluru, and Bhubaneswar. Later on, we’ll extend to Ahmedabad, Gangtok, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Indore, Kochi, Lucknow Patna, and Shimla. Our scope of the pilot may be expanded gradually to include more banks and users if needed
They are basically like currencies in digital form, so you would see them as liabilities or currency in circulation in the Reserve Bank of India’s balance sheet. It can also be exchangeable with regular currency notes and themselves.
Type of CBDC
RBI, central bank offer two types of CBDCs
a. General-purpose or retail
b. Wholesale.
Retail CBDC will be able to be used for general transactions, like paying for things at a store. And wholesale CBDC will be for settlement transfers, like between banks. This is significant because it can have a great effect on the country’s overall digital economy and bring in more financial inclusion.
Advantages of the e-Rupee
1. The e-Rupee is a more efficient and convenient way to transact than the traditional paper Rupee.
2. The e-Rupee is less prone to counterfeiting than the paper Rupee.
3. The e-Rupee can be used to make payments online, eliminating the need for cash or check transactions.
4. The e-Rupee provides greater security for both buyers and sellers during transactions.
5. The e-Rupee offers a faster, more convenient way to send money internationally than using traditional wire transfer services.
How is the e-Rupee different from the regular Rupee?
The e-Rupee is a digital version of the regular Rupee, which can be used to make payments online or offline. It is similar to the regular Rupee in terms of value and purchasing power.
The main difference between the two is that the e-Rupee is not physical currency, but rather a digital representation of the Rupee. This means that it can be stored on your electronic device (such as a smartphone or computer) and used to make payments without the need for paper money.
The e-Rupee also has some additional features, such as the ability to send money to other users and track your spending, which is not available with regular currency.
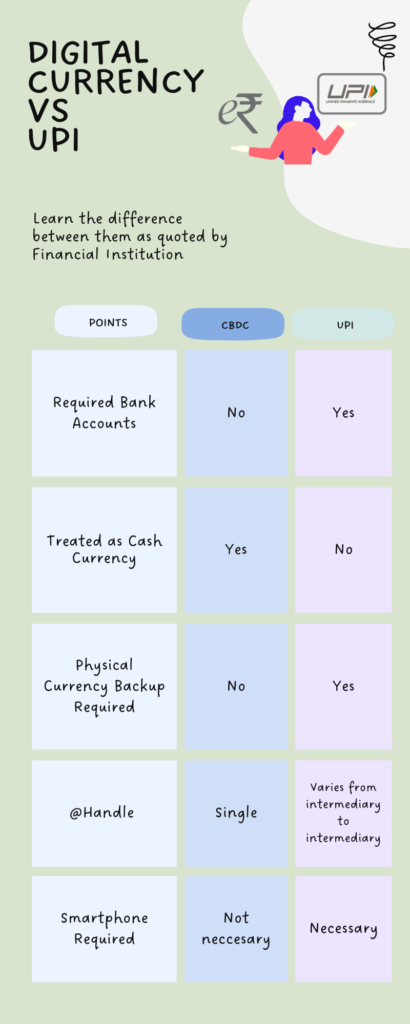
Difference between Digital Currency and UPI Payments
Frequently Asked Question
The idea is to complement current forms of money by providing users with an additional way of payment, which would be in addition to the existing ones. The digital rupee as conceived by RBI shall provide all the convenience, accessibility and affordability associated with paper money.
India’s micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) often have difficulty getting loans. Central bank-issued digital currency could help in a variety of ways. First, it can provide lending the MSMEs need to sustain themselves during economic downturns. Second, central banks could use their digital currencies to alleviate the cash flow constraints that make business more difficult for SMEs. Thirdly, banks will be able to better assess borrowers’ credit risk profiles once they’re using digital currency
Some experts say that the CBDC for retail might be based on Distributed Ledger Technology, rather than the blockchain. The transparency and the automation capabilities will give participants a clear view of what is happening within transactions, which would speed up financial activity for retail payments in general.
Experts are predicting that there could be interchangeability between a CBDC and cash transactions. This would create an opt-in opt-out system for the CBDC.
Digital Rupee may make it easy to collect taxes through smart contracts, but there are various other developments in law and policy which would be required before a full retail rollout.
CBDCs can also be used for retail payments.Payment instruments could be made available to pay with CBDC. Retail CBDC distributed by the RBI and commercial banks would have to be placed in electronic wallets or accounts by the end users.
Digital Rupee would enable payment means between the following:
a. Consumer to consumer ie C2C
b. Consumer to business ie C2B
c. Business to business ie B2B
There are some concerns about the private keys of the Digital Rupee and the risks associated with losing one. However, it seems likely that Digital Rupee would not be self-custodial.
With digital Rupees, all of the transactions will be traceable. Experts say that tracking CBDCs can help businesses prove their creditworthiness to retailers and other institutions.
Conclusion.
The e-Rupee is a new, digital version of the Indian Rupee that is intended to make transactions more efficient and secure. While the e-Rupee is still in its early stages, it has great potential to revolutionize the way we think about and use money. With its ability to be easily converted into other currencies, the e-Rupee could very well become the global standard for currency. Only time will tell how successful the e-Rupee will be, but it is definitely an exciting development worth keeping an eye on.
The e-Rupee is a new generation of the Indian Rupee that is designed to be more efficient and secure. It is important to know all about the e-Rupee so that you can make the most out of it. With the e-Rupee, you will be able to transact with ease and convenience.


